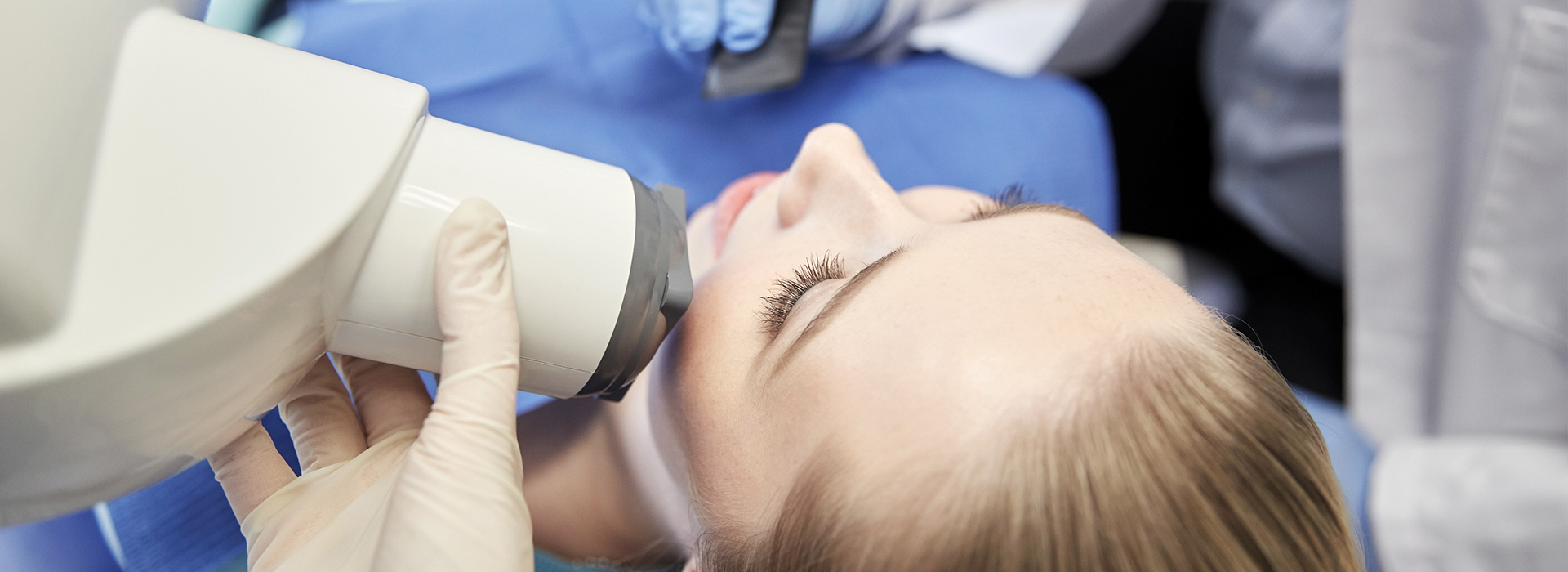
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and computer processing to create dental images. A small, flat sensor or a specialized scanning device picks up X-ray data, which is then converted into a digital file and displayed on a monitor within seconds. Because the system captures and processes information more efficiently than film, it requires a lower X-ray dose to produce clear diagnostic images.
The speed of this workflow matters for both patients and clinicians. Rather than waiting for film to develop, the team can review images immediately, adjust positioning if needed, and repeat a shot with minimal delay and minimal additional exposure. This immediacy helps keep appointments on schedule and reduces the time a patient spends in the chair.
Sensors and software continue to evolve, giving clinicians tools such as adjustable contrast, zoom, and measurement overlays that sharpen details without extra radiation. These enhancements allow the practice to tailor the image to the diagnostic task at hand — for example, fine-tuning contrast to reveal early decay or magnifying root anatomy for endodontic planning.
One of the most important benefits of digital radiography is reduced radiation exposure compared with conventional film techniques. Advances in sensor sensitivity and image processing mean clinicians can obtain diagnostically useful images with a smaller dose of radiation. This reduction is particularly relevant for patients who require periodic imaging, children, and those with heightened sensitivity to radiation.
Comfort is also improved. Digital sensors are thinner and more ergonomically shaped than older film packets, making intraoral images more tolerable. Because images appear instantly, patients spend less time with sensors in their mouths and fewer retakes are necessary when positioning is correct.
From an environmental standpoint, digital systems eliminate the need for chemical developers and film disposal, reducing the practice’s ecological footprint. The elimination of chemical processing not only streamlines office workflow but also supports safer handling and storage of clinical materials.
Digital radiography enhances diagnostic accuracy by producing high-resolution images that clinicians can manipulate to highlight problem areas. Software tools allow for incremental adjustments of brightness and contrast, side-by-side comparisons, and precise measurements that aid in detecting early cavities, monitoring bone levels, and assessing root and tooth structure.
These capabilities are particularly valuable when planning complex care. For example, images can be used to evaluate the bone supporting a tooth, identify hidden decay between teeth, or assist with root canal evaluation. The ability to review images together during a consultation helps patients understand their condition and the rationale behind recommended treatments.
Because images are stored digitally, clinicians can track changes over time by comparing successive radiographs. This longitudinal view supports preventive strategies and helps the team make informed decisions about when to intervene and when to continue monitoring.
Digital radiography naturally integrates with electronic health records, digital impressions, and other in-office technologies to create a cohesive patient file. Images are saved directly to the patient’s chart, where they can be accessed during appointments, referenced in treatment planning, or included in referrals to specialists. This connectivity improves coordination of care and reduces administrative delays.
In cases where collaboration is needed — for example, with oral surgeons, orthodontists, or radiology centers — digital files can be shared quickly and securely. This speeds up consultations and helps ensure that all providers are working from the same high-quality images, improving continuity and accuracy in multi-disciplinary care.
The software tools that accompany digital radiography also support patient education. Clinicians can annotate images, zoom in on areas of concern, and present visual explanations that make complex anatomy easier to understand. When patients see clear visuals tied to clinical findings, they can make more informed decisions about their care.
If you’ve never had digital dental X-rays, the process is straightforward and fast. A member of the clinical team will position the sensor in the mouth or use an external unit for panoramic images, then step behind a shield or out of the room briefly while the image is taken. The exposure time is typically very short, and many images are captured in a matter of seconds.
Because the images appear immediately on the monitor, your clinician will often review them with you during the same visit. This immediate feedback allows for quicker diagnoses and timely discussions about next steps, whether that’s a preventive measure, a restorative procedure, or a follow-up observation.
Special considerations, such as positioning for children or patients with a strong gag reflex, are handled with care. The clinical team uses gentle techniques and adjustments to make the experience as comfortable as possible while still obtaining the diagnostic images required to provide safe, effective care.
At Newpoint Family Dental, we view digital radiography as a core component of modern, patient-centered dentistry. It supports safer imaging, clearer diagnoses, and better communication between clinicians and patients. If you’d like to learn more about how we use digital X-rays during examinations and treatment planning, please contact us for more information.
Digital radiography uses electronic sensors and computer processing to capture dental images instead of traditional film. A small intraoral sensor or external scanning device records X-ray data that is immediately converted into a digital file and displayed on a monitor for rapid review. Because data capture and processing are more efficient, clinicians obtain clear diagnostic images without film development delays.
Compared with film, digital systems typically require a lower X-ray dose to achieve useful images and eliminate chemical processing and film storage. Software enhancements let clinicians fine-tune contrast, magnification and measurements to reveal details that might be harder to see on conventional film. The faster workflow also reduces chair time and the need for repeat exposures when positioning needs adjustment.
Digital dental X-rays are considered safe when used according to established clinical guidelines because they generally require less radiation than conventional film techniques. Modern sensors are more sensitive and image-processing tools can produce diagnostic-quality images with smaller exposures. Protective measures such as lead aprons and careful collimation further minimize exposure to surrounding tissues.
Clinicians follow protocols to balance diagnostic benefit and radiation risk, taking images only when needed for diagnosis, treatment planning or monitoring. Staff training, routine equipment maintenance and proper positioning all contribute to safe imaging practices. If you have specific concerns about radiation, discuss them with your dental team so they can explain the rationale for recommended images.
Digital radiography produces high-resolution images that can be manipulated to highlight areas of interest, improving the detection of cavities, bone changes and root anatomy. Tools for adjusting brightness and contrast, zooming and adding measurement overlays help clinicians evaluate problems with greater precision. Side-by-side comparisons of images also make it easier to identify subtle changes over time.
These capabilities support more accurate treatment planning for restorative work, endodontics and implant placement by providing clearer visual information about tooth and bone structure. Digital images stored in the patient record enable longitudinal tracking to determine when intervention is needed versus continued observation. The result is better-informed clinical decisions and more predictable outcomes.
The procedure is straightforward and usually quick: a clinician will position a thin digital sensor inside your mouth or use an external unit for panoramic images, then take the exposure while briefly standing behind a shield. Exposure times are short and many images are captured in seconds, so the overall appointment impact is minimal. Sensors are thinner and more ergonomically shaped than older film packets, which often improves comfort during intraoral imaging.
Because images appear instantly on a monitor, your clinician can review them with you during the same visit and explain findings visually. If positioning needs adjustment, a repeat can be performed quickly with minimal additional exposure. Special positioning techniques and gentle handling are used for children and patients with a strong gag reflex to make the process as comfortable as possible.
Digital radiographs integrate seamlessly with electronic health records, digital impressions and CAD/CAM systems to create a unified patient file that supports comprehensive treatment planning. Images save directly to the patient chart and can be used in conjunction with intraoral scans, CEREC restorations and implant planning software. This interoperability reduces administrative steps and helps ensure all clinical data are available when making treatment decisions.
Integration also enhances patient communication by allowing clinicians to present annotated images alongside scans and treatment simulations during consultations. When specialists are involved, digital files streamline referrals and collaborative planning. The combined technology ecosystem leads to more coordinated care and a clearer explanation of treatment options for patients.
Yes, digital radiographs can be shared securely with specialists, labs or other providers to support coordinated care when referrals or collaborative planning are needed. Files are transferred through secure, encrypted systems or shared directly from the patient record to ensure that only authorized recipients access the images. Clinicians typically obtain patient consent before sending images outside the practice as part of routine referral protocols.
Patient privacy is protected by storing images in the electronic chart and using secure networks for transmission, with access restricted to staff who require the information for treatment. Practices follow applicable privacy and security standards to manage patient records and imaging files. If you have questions about how your images will be handled or shared, your dental team can explain their policies in detail.
The frequency of dental X-rays is individualized based on factors such as age, oral health status, risk for decay, previous dental work and current symptoms. Patients with active dental problems or a history of extensive restorations may require imaging more often than those with low risk and stable oral health. Clinicians use prior images and a clinical examination to determine whether new radiographs are necessary for diagnosis or monitoring.
Routine imaging intervals are guided by professional recommendations and tailored to each patient’s needs to avoid unnecessary exposure while ensuring timely detection of issues. Your dentist will review your dental history and risk factors during visits and recommend radiographs only when they add clear diagnostic value. Open communication about concerns and symptoms helps the team decide on appropriate imaging intervals.
Digital X-rays typically use lower radiation doses than traditional film, which is beneficial for children who may require more frequent monitoring and for patients with specific sensitivities. Clinicians apply pediatric techniques, smaller sensors and targeted exposure settings to further reduce dose for younger patients. For pregnant patients or those who suspect pregnancy, dental teams follow established guidelines and generally postpone nonurgent imaging or take extra precautions to minimize exposure.
Protective measures such as lead aprons and thyroid collars are used when appropriate, and clinicians weigh the diagnostic need against any potential risk before proceeding. If imaging is necessary during pregnancy, the team will take steps to limit exposure and explain the rationale. Discuss any pregnancy concerns with your dental provider so they can tailor care accordingly.
Image enhancement tools allow clinicians to adjust contrast and brightness, magnify areas of interest and add measurement overlays that clarify anatomical details on radiographs. These adjustments can make early decay, bone loss or root anatomy easier to see and interpret, improving diagnostic confidence. The ability to compare enhanced images side by side helps clinicians identify changes that might be missed on unaltered images.
For patients, enhanced images provide clear visuals that support explanations of findings and recommended treatments, making complex information easier to understand. Clinicians can annotate and point out specific concerns during consultations so patients see exactly what the team observes. This visual context helps patients make informed decisions and participate more actively in their care.
At Newpoint Family Dental, we use digital radiography to improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce radiation exposure and streamline patient care within the office. The technology supports faster image acquisition, enhanced visualization and easier integration with electronic records and other digital workflows. These advantages help clinicians make timely, well-informed treatment recommendations during the appointment.
Digital imaging also supports clearer communication with patients by allowing side-by-side comparisons, annotations and visual explanations that make treatment plans easier to understand. Eliminating chemical processing reduces environmental impact and simplifies image storage and retrieval. If you would like to learn more about how we use digital X-rays during exams, our team can explain protocols and answer specific questions.
Our mission is to help every patient enjoy healthy teeth and a confident smile, providing care that meets your needs and exceeds expectations.
